How 3D LiDAR Scanning Prevents Accidents in Construction: Safer Sites with Smarter Tech

Introduction
The construction industry has always been a cornerstone of economic development, driving urban growth and infrastructure advancement. However, with this rapid expansion comes a sobering reality: construction sites are among the most hazardous workplaces worldwide. According to reports from organizations such as the International Labour Organization (ILO) and government safety boards, thousands of construction-related accidents occur every year, ranging from minor injuries to fatalities caused by falls, collisions, or structural failures. In India, the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) highlighted that accidental deaths at worksites, particularly in construction, have been steadily increasing, calling for urgent technological interventions in safety management.
Government Insights on Construction Accidents
Construction accidents remain a major concern for governments worldwide. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA, USA), one in five worker deaths in the U.S. occurs in construction. The leading causes, often referred to as the “Fatal Four”, are falls, being struck by objects, electrocution, and being caught in or between machinery. Eliminating these could save hundreds of lives annually.
In India, the NCRB’s Accidental Deaths and Suicides in India (ADSI) Report reveals that the construction sector is among the top contributors to workplace fatalities. Many incidents are caused by structural collapses, unsafe scaffolding, lack of protective equipment, and inadequate monitoring of hazardous zones.
The National Safety Stand-Down to Prevent Falls in Construction focuses on identifying fall hazards and underscores the importance of fall prevention within the construction industry. This year, the National Safety Stand-Down is being observed this year May 5 to May 9, 2025.
In 2023, approximately 20.8 percent of workplace deaths occurred in the construction industry, with 38.5 percent of those fatalities resulting from falls, slips, and trips. Additionally, the construction sector was responsible for 47.8 percent of all fatal falls, slips, and trips that year.
United States:
- In 2023, out of 1,075 total construction fatalities in the U.S., 421 were due to falls from a lower level, translating to 39.2% of all fatalities.
- Overall, construction workers face significantly higher risks, with a fatality rate of 13 per 100,000 workers, compared to 3.7 per 100,000 across all occupations.
India:
- A 2016 study estimated that of the nearly 48,000 occupational fatalities annually in India, approximately 24.2% are attributed to the construction sector.
- Projected fatality numbers in the Indian construction industry range from 11,614 to 22,080 per year, based on modeling using cement consumption and workforce data.
- As a result, the construction sector in India has one of the highest fatality rates, estimated at 0.22 deaths per 1,000 workers per year, compared to just 0.05 in railways, 0.09 in factories, and 0.24 in coal mines.
As governments and industry leaders push for smart construction practices, technologies like 3D LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) are emerging as critical tools for accident prevention. By enabling real-time monitoring, precision mapping, and hazard detection, LiDAR is reshaping how contractors, engineers, and architects approach safety on construction sites.
What is LiDAR?
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances with high accuracy. By emitting laser beams and analyzing their reflection, LiDAR systems generate precise 3D maps of an environment, often referred to as “point clouds.” These point clouds can capture minute details of terrain, structures, and objects in real time.
The global LiDAR market is expanding rapidly due to its increasing applications in infrastructure, safety, and smart city projects. According to MarketsandMarkets, the LiDAR market size is projected to grow from USD 3.27 billion in 2025 to over USD 12.79 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of more than 31.3%.
LiDAR is widely used in industries such as autonomous vehicles, archaeology, urban planning, and forestry, but its role in construction has gained momentum in recent years. On a construction site, LiDAR systems can be mounted on drones, vehicles, or tripods to capture accurate, real-time spatial data. This data helps construction managers identify potential hazards, monitor progress, and ensure worker safety.
Let’s we will explore how 3D LiDAR scanning helps prevent accidents on construction sites.
How 3D LiDAR Scanning Prevents Accidents in Construction Sites
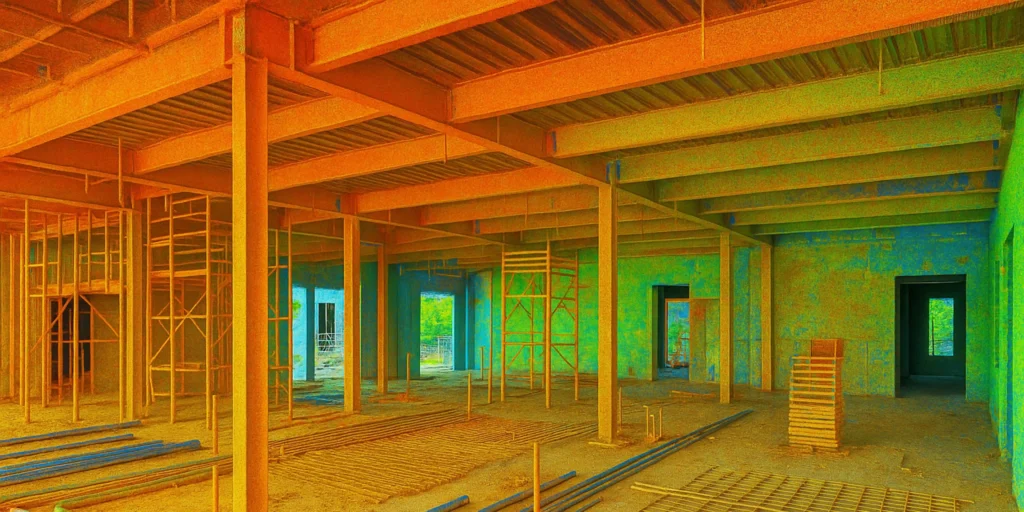

The integration of 3D LiDAR scanning in construction safety is proving transformative. Unlike traditional methods of manual inspections or basic camera surveillance, LiDAR offers real-time, high-precision, 360-degree monitoring of construction sites. Here’s how it helps prevent accidents:
1. Real-Time Hazard Detection
LiDAR can continuously scan the site to detect unstable surfaces, misplaced equipment, or unauthorized personnel in restricted zones. This data can be integrated with alarms or worker wearables, immediately warning staff before accidents occur.
2. Monitoring Worker Safety in Hazardous Areas
Using LiDAR, supervisors can track worker movements in high-risk zones such as scaffolding, excavation pits, or high-rise structures. If workers approach unsafe areas without proper gear, alerts can be triggered to prevent accidents.
3. Preventing Collisions with Machinery
Heavy machinery such as cranes, excavators, and trucks often pose collision risks. LiDAR systems can monitor equipment blind spots and create virtual safety perimeters, reducing the chance of accidents involving workers or vehicles.
4. Structural Stability Assessment
LiDAR-generated 3D scans can detect minute shifts in scaffolding, concrete formworks, or temporary structures. Early identification of structural weaknesses helps prevent collapses, one of the leading causes of construction fatalities.
5. Enhanced Emergency Response
In case of an incident, LiDAR data provides real-time site mapping, enabling rescue teams to navigate efficiently. This can significantly reduce response times and save lives.
6. Integration with BIM (Building Information Modeling)
LiDAR data can be integrated into BIM systems to compare actual site conditions with planned models. Discrepancies such as uneven surfaces, material misplacement, or deviations in structural alignment can be flagged early, preventing potential hazards.
Conclusion
By enabling real-time hazard detection, monitoring worker movements, preventing machinery collisions, and assessing structural stability, LiDAR is revolutionizing safety practices on construction sites.
At the forefront of this change, ProtoTech Solutions is helping the construction industry embrace 3D measurement and LiDAR-based applications to ensure safer project execution. With its expertise in 3D visualization, CAD/CAE tool development, AI-powered measurement solutions, and BIM modeling, and CAD design and drafting. ProtoTech empowers architects, engineers, and contractors to gain accurate site insights, mitigate risks, and create safer workplaces.
In construction, as-built drawings are detailed records of the final dimensions, layouts, and specifications of a project after completion. Unlike design blueprints, which show what was intended to be built, as-built documentation captures the exact conditions on site, including modifications made during construction. When generated with 3D LiDAR scanning, as-builts become significantly more accurate and valuable.